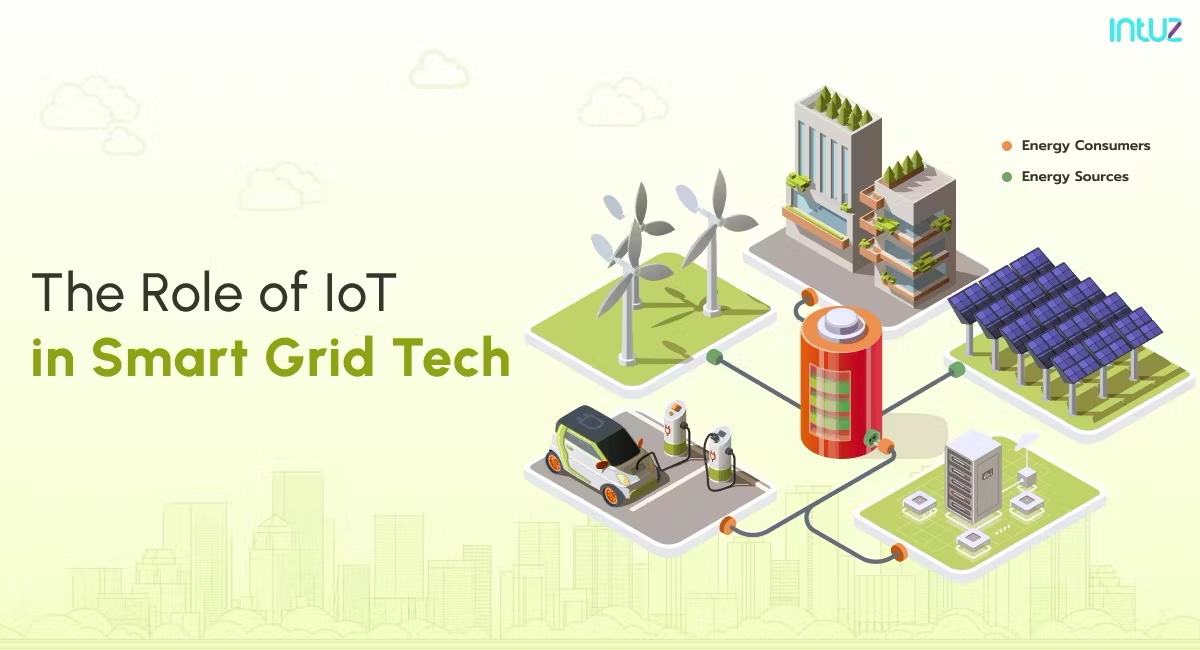
The Internet of Things (IoT) is rapidly transforming numerous industries, and electrical distribution is no exception. By connecting devices and systems, IoT technology is revolutionizing how we monitor, manage, and optimize electrical networks. This integration is ushering in an era of unprecedented efficiency, reliability, and proactive maintenance, ultimately leading to a more resilient and sustainable electrical grid. The potential for IoT to reshape the electrical distribution landscape is immense, offering solutions to long-standing challenges and paving the way for future innovations. One of the most significant impacts of IoT in electrical distribution is enhanced monitoring and diagnostics. Smart sensors deployed throughout the grid can provide real-time data on voltage, current, temperature, and other critical parameters. This data can be used to identify anomalies, predict equipment failures, and optimize power flow. Remote monitoring capabilities enable utilities to detect and respond to outages more quickly, minimizing downtime and improving customer satisfaction. Predictive maintenance, powered by IoT data analytics, can prevent equipment failures before they occur, reducing maintenance costs and improving grid reliability. IoT also enables the development of smart grids, which are more efficient and responsive than traditional electrical networks. Smart meters, connected devices, and advanced control systems allow for two-way communication between utilities and consumers. This enables demand response programs, which can help balance supply and demand, reducing peak load and improving grid stability. IoT-enabled automation can also optimize power distribution, reducing energy losses and improving overall grid efficiency. The transition to smart grids is crucial for accommodating the increasing adoption of renewable energy sources and electric vehicles. Furthermore, IoT is driving innovation in asset management. By tracking the location and condition of electrical equipment, utilities can optimize maintenance schedules and reduce the risk of equipment failures. Smart sensors can also monitor the performance of transformers, substations, and other critical infrastructure, providing valuable insights into their operational status. This data can be used to improve asset utilization, extend equipment lifespan, and reduce maintenance costs. IoT-enabled asset management is essential for ensuring the long-term reliability and sustainability of the electrical grid. The role of IoT extends to improving safety in electrical distribution. Smart sensors can monitor for potential hazards, such as arc flash incidents or equipment overheating, and provide real-time alerts to workers. Wearable IoT devices can also enhance worker safety by providing location tracking, fall detection, and other safety features. This technology not only protects workers but also improves overall safety compliance. The data collected by IoT devices can be used to analyze safety trends and identify areas for improvement. In conclusion, IoT is transforming electrical distribution by enhancing monitoring, enabling smart grids, optimizing asset management, and improving safety. As the technology continues to evolve, we can expect even greater advancements in the efficiency, reliability, and sustainability of our electrical infrastructure. Embracing IoT is essential for building a resilient and future-proof electrical grid that can meet the growing demands of our increasingly connected world.
The Role of IoT in Electrical Distribution
IoT is revolutionizing electrical distribution by enabling real-time monitoring, smart grid development, optimized asset management, and enhanced safety through connected devices and data analytics.